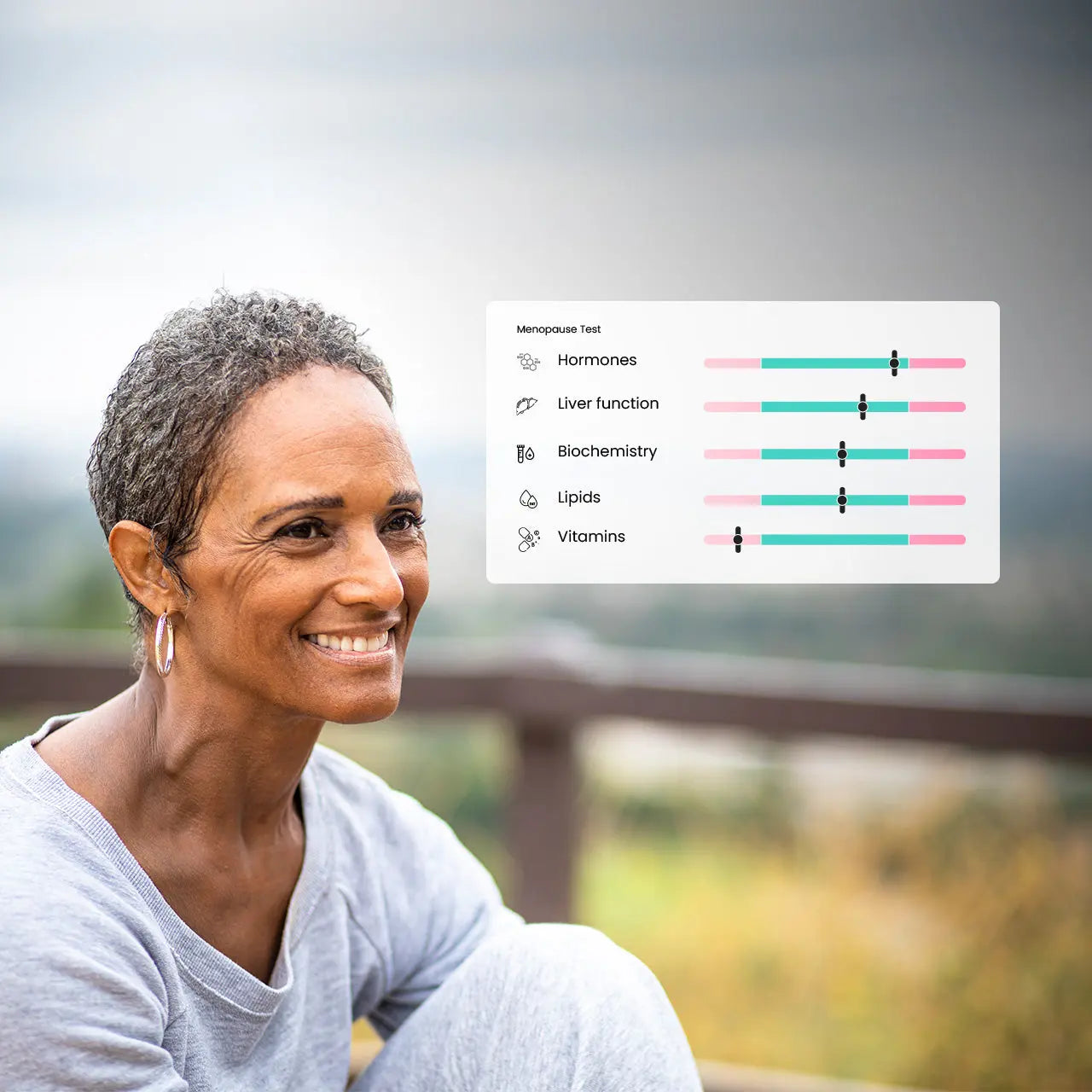
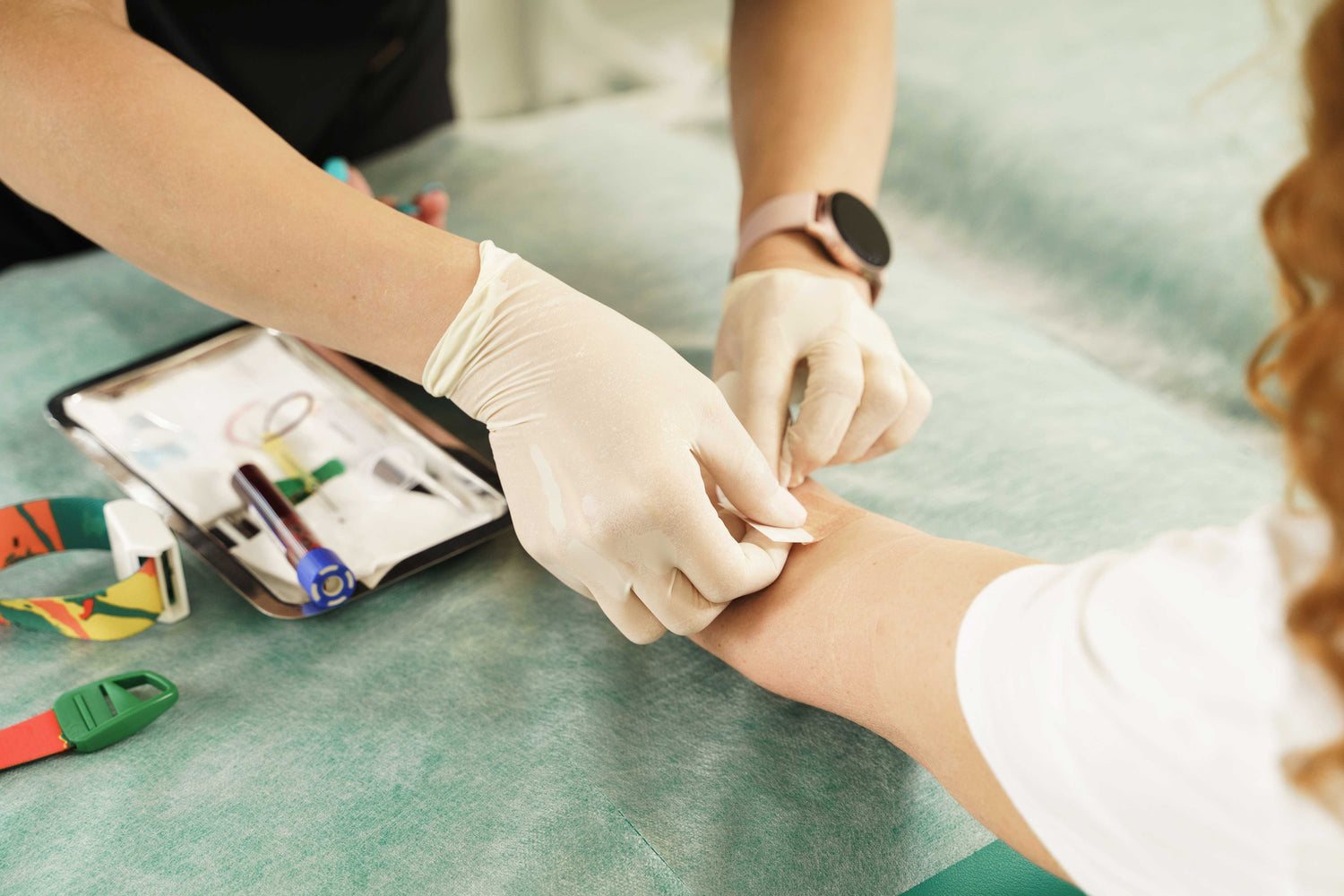
Menopause
Menopause
-
All of our nurses & phlebotomists have
- Valid DBS (Background Check)
- Experience of at least 100 sample collections
- Health & Safety Training
- Infection Control Training
- Safeguarding Training
- Malpractice Insurance
-
NHS Trusted Labs
-
Our doctors provide reviews but do not offer consultations, medical advice, or diagnoses. Reviews are available through the app or email.
-
This timeline begins once the lab receives the sample.
-
99.8% Reliable
-
Couldn't load pickup availability






What gets tested?
Menopause
This transition phase in a woman's life can bring about numerous physiological changes, and this 31 biomarker test helps in assessing those changes, potential health risks, and areas of concern. Understanding the impact is the best way to learn how to handle these changes
Blood Analysis
- Albumin: The main protein in blood plasma, important for maintaining blood volume and pressure. Why measure: To assess liver function and overall protein levels.
- Ferritin: A protein that stores and releases iron, indicating the body's iron reserves. Why measure: To evaluate iron levels and diagnose iron deficiency or overload.
Bone Health
- Calcium: A crucial mineral for maintaining bone strength and supporting various bodily functions. Why measure: Essential for bone health and metabolic processes.
- Corrected Calcium: Calcium level adjusted based on albumin concentration to provide a more accurate measurement of calcium status. Why measure: To ensure accurate assessment of calcium levels in conditions affecting albumin.
Cardiovascular Health
- Cholesterol: A fatty substance essential for building cell membranes and producing hormones. Why measure: To evaluate overall cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health.
- Chol:HDL Ratio: The ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol, indicating cardiovascular risk. Why measure: To evaluate heart disease risk and lipid balance.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol: Known as "good" cholesterol, it helps lower the risk of cardiovascular disease by removing excess cholesterol from the bloodstream. Why measure: To assess protective cardiovascular benefits and risk factors.
- HDL Cholesterol Ratio: The ratio of HDL cholesterol to total cholesterol, providing insight into cardiovascular risk. Why measure: To gauge the balance between good and total cholesterol and assess cardiovascular health.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol: Referred to as "bad" cholesterol, it can lead to plaque buildup in arteries and increase cardiovascular risk. Why measure: To monitor and manage cardiovascular risk.
- Non-HDL Cholesterol: Total cholesterol minus HDL cholesterol, representing all "bad" cholesterol types. Why measure: To assess cardiovascular risk beyond LDL cholesterol.
- Triglycerides: A type of fat in the blood that can contribute to coronary artery disease if levels are elevated. Why measure: To assess risk of heart disease and evaluate lipid management.
Diabetes
- HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin): A blood biomarker that reflects the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It is widely used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. Why measure: To manage and diagnose diabetes effectively.
Inflammation
- HsCRP (High-sensitivity C-reactive Protein): A marker of inflammation that can indicate increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Why measure: To predict cardiovascular disease risk and inflammation levels.
Reproductive Hormones
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Regulates reproductive processes such as egg development in females. Why measure: To assess reproductive health and diagnose fertility issues.
- Luteinising Hormone (LH): Regulates ovulation in females. Why measure: To evaluate reproductive health and diagnose hormonal disorders.
- Progesterone: A hormone that plays a role in reproductive health, hormone balance, and overall well-being.Why measure: To evaluate menstrual health, fertility, and pregnancy in women, and to assess hormonal balance and prostate health in men
- Prolactin: Involved in lactation and reproductive health. Why measure: To assess lactation, pituitary function, and reproductive health.
Sex Steroid Hormones
- DHEA-S (Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulphate): An androgen precursor produced by the adrenal glands, which plays a role in the production of sex hormones and impacts various bodily functions. Why measure: To evaluate adrenal gland function, assess androgen status, and diagnose conditions related to hormonal imbalances, such as adrenal insufficiency or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Oestradiol (Estradiol): A key form of estrogen important for regulating the menstrual cycle and reproductive health. Why measure: To assess estrogen levels and diagnose hormonal disorders.
- Testosterone: Main male sex hormone involved in male characteristics, muscle mass, and libido. Why measure: To evaluate androgen levels and diagnose hormonal imbalances or conditions.
- Free Testosterone (Calculated): The biologically active form of testosterone. Why Measure: To assess testosterone levels and diagnose hormonal imbalances.
- Free Androgen Index (FAI): Ratio of total testosterone to SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin), indicating bioavailable testosterone. Why measure: To evaluate androgen status and diagnose related hormonal disorders.
- SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin): A protein that binds sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen. Why measure: To assess hormonal balance and diagnose related disorders.
Stress Hormones
- Cortisol: Primary stress hormone that regulates metabolism, immune response, and stress adaptation. Why Measure: To evaluate stress levels, adrenal function, and overall hormonal balance.
Thyroid Function
- FT3 (Free Triiodothyronine): The unbound form of T3 hormone that is active in regulating metabolism and energy levels. Why measure: To assess thyroid function and diagnose thyroid disorders.
- FT4 (Free Thyroxine): The unbound form of T4 hormone that helps regulate metabolism and growth. Why measure: To evaluate thyroid function and diagnose thyroid-related conditions.
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): A hormone that regulates the production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) by the thyroid gland. Why measure: To evaluate thyroid function and diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Vitamins and Minerals
- Active B12: The form of vitamin B12 that is available for use by the body, essential for blood cell production and nerve function. Why measure: To assess vitamin B12 levels and diagnose deficiencies or related conditions.
- Magnesium: A mineral important for muscle and nerve function, bone health, and energy production. Why measure: To assess magnesium levels and diagnose deficiencies or related health conditions.
- Vitamin D: Vital for calcium absorption and bone health, playing a key role in maintaining bone density. Why measure: To assess and support optimal bone health and calcium metabolism.
- Serum Folate (Vitamin B9): A vitamin important for DNA synthesis and cell division, and crucial for preventing certain birth defects. Why measure: To evaluate folate levels and diagnose deficiencies or related health issues.
About this test
- Hot flashes or night sweats
- Mood swings or irritability
- Sleep disturbances or waking up tired
- Unexplained weight gain, especially around the midsection
- Low libido or vaginal dryness
- Brain fog or memory issues
- Increased joint pain or stiffness
A focused test for women transitioning through menopause. Ideal for those managing symptoms or assessing long-term hormonal changes.
- Estrogen imbalance
- Bone density loss
- Cardiovascular risk factors
Symptoms
- Hot flashes or night sweats
- Mood swings or irritability
- Sleep disturbances or waking up tired
- Unexplained weight gain, especially around the midsection
- Low libido or vaginal dryness
- Brain fog or memory issues
- Increased joint pain or stiffness
Who should be test
A focused test for women transitioning through menopause. Ideal for those managing symptoms or assessing long-term hormonal changes.
When to test
- Estrogen imbalance
- Bone density loss
- Cardiovascular risk factors
What's measured
Testosterone
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a key role in the development of secondary sex characteristics, fertility, muscle strength, and bone health.
Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG)
SHBG is a type of protein produced by your liver, which is responsible for transporting testosterone and some other hormones through the bloodstream. SHBG levels that are too high or too low can be a sign that there is to much or or little amounts of certain hormones for your body to use.
Free Androgen Index (FAI)
The FAI is not a measure of a particular hormone, but a comparison of the total amount of testosterone in your blood compared to your levels of SHBG. FAI can help indicate how much free testosterone is available for your body to use.
Our process
How it all works?
step 1
Choose your test
The user or the partner selects one of Lola's existing tests, each assigned a unique code linking the test to the partner. This code ensures proper tracking for referrals, results access, or both, depending on the partnership type.

step 2
Choose a date/time for sample collection
The user schedules a sample collection during checkout, choosing from Lola's available options (at home, clinic visits) or opts for the partner to perform the blood draw if their partnership supports it.

step 3
Blood sample taken and sent to Lab
Samples are analysed at our CQC-compliant and NHS-standard labs, providing accurate and detailed breakdowns for each test.
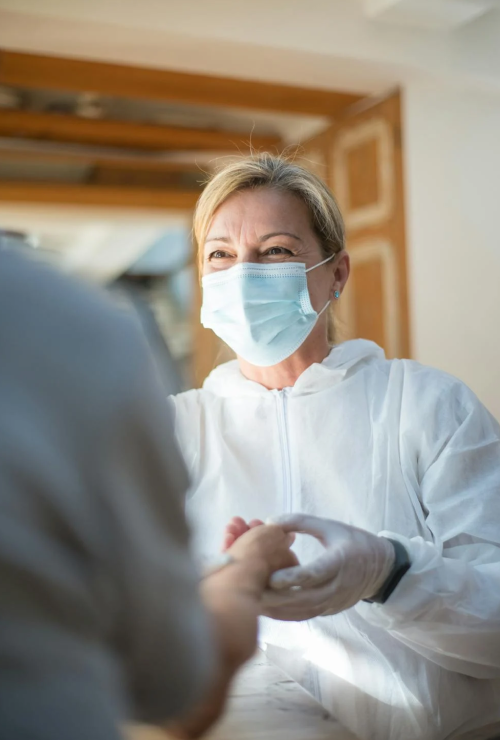

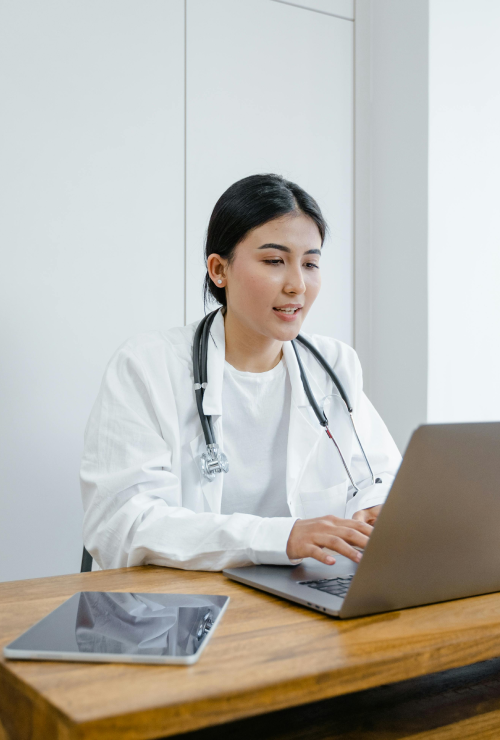
step 4
Personalised Doctor Review
Results are made available through Lola's intuitive partner portal, complete with actionable insights and customisable reporting options for the partner and user.





Includes 56 key biomarkers, providing a thorough assessment of blood health, organ function, chronic disease risk, and overall well-being.
-
56 Biomarkers
Learn more -
All of our nurses & phlebotomists have
- Valid DBS (Background Check)
- Experience of at least 100 sample collections
- Health & Safety Training
- Infection Control Training
- Safeguarding Training
- Malpractice Insurance
-
This timeline begins once the lab receives the sample.
Covers 45 essential biomarkers to assess cholesterol, diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, anemia, heart disease, hormone levels, inflammation, and overall nutrition
-
45 Biomarkers
Learn more -
All of our nurses & phlebotomists have
- Valid DBS (Background Check)
- Experience of at least 100 sample collections
- Health & Safety Training
- Infection Control Training
- Safeguarding Training
- Malpractice Insurance
-
This timeline begins once the lab receives the sample.
Evaluates 70 critical biomarkers for the most comprehensive health assessment, focusing on advanced cardiovascular, hormonal, metabolic, and immune markers.
-
70 Biomarkers
Learn more -
All of our nurses & phlebotomists have
- Valid DBS (Background Check)
- Experience of at least 100 sample collections
- Health & Safety Training
- Infection Control Training
- Safeguarding Training
- Malpractice Insurance
-
This timeline begins once the lab receives the sample.
Analyzes 62 biomarkers for a full health profile, including cardiovascular health, metabolic function, hormone balance, and autoimmune conditions.
-
62 Biomarkers
Learn more -
All of our nurses & phlebotomists have
- Valid DBS (Background Check)
- Experience of at least 100 sample collections
- Health & Safety Training
- Infection Control Training
- Safeguarding Training
- Malpractice Insurance
-
This timeline begins once the lab receives the sample.
What gets tested
Complete panel for your health
Blood Analysis
Albumin: The main protein in blood plasma, important for maintaining blood volume and pressure. Why measure: To assess liver function and overall protein levels.
Ferritin: A protein that stores and releases iron, indicating the body's iron reserves. Why measure: To evaluate iron levels and diagnose iron deficiency or overload.
Bone Health
Calcium: A crucial mineral for maintaining bone strength and supporting various bodily functions. Why measure: Essential for bone health and metabolic processes.
Corrected Calcium: Calcium level adjusted based on albumin concentration to provide a more accurate measurement of calcium status. Why measure: To ensure accurate assessment of calcium levels in conditions affecting albumin.
Cardiovascular Health
Cholesterol: A fatty substance essential for building cell membranes and producing hormones. Why measure: To evaluate overall cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health.
HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol: Known as "good" cholesterol, it helps lower the risk of cardiovascular disease by removing excess cholesterol from the bloodstream. Why measure: To assess protective cardiovascular benefits and risk factors.
Chol:HDL Ratio:The ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol, indicating cardiovascular risk.Why measure:To evaluate heart disease risk and lipid balance.
HDL:Cholesterol Ratio: The ratio of HDL cholesterol to total cholesterol, providing insight into cardiovascular risk. Why measure: To gauge the balance between good and total cholesterol and assess cardiovascular health.
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol: Referred to as "bad" cholesterol, it can lead to plaque buildup in arteries and increase cardiovascular risk. Why measure: To monitor and manage cardiovascular risk.
Non-LDL Cholesterol: This measurement represents total cholesterol minus LDL cholesterol, including other lipoproteins like HDL and VLDL. Why measure: It offers a clearer view of cardiovascular risk by highlighting potentially harmful cholesterol levels. Higher non-LDL cholesterol may indicate increased risk, making it important for monitoring heart health
Triglycerides: A type of fat in the blood that can contribute to coronary artery disease if levels are elevated. Why measure: To assess risk of heart disease and evaluate lipid management.
Diabetes
HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin): A blood biomarker that reflects the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It is widely used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. Why measure: To manage and diagnose diabetes effectively.
Inflammation
HsCRP (High-sensitivity C-reactive Protein): A marker of inflammation that can indicate increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Why measure: To predict cardiovascular disease risk and inflammation levels.
Reproductive Hormones
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Regulates reproductive processes such as egg development in females and sperm production in males. Why Measure: To assess reproductive health and diagnose fertility issues.
Luteinising Hormone (LH): Regulates ovulation in females and testosterone production in males. Why Measure: To evaluate reproductive health and diagnose hormonal disorders.
Progesterone: A hormone that plays a role in reproductive health, hormone balance, and overall well-being. Why measure: To evaluate menstrual health, fertility, and pregnancy in women, and to assess hormonal balance and prostate health in men.
Prolactin: Involved in lactation and reproductive health. Why Measure: To assess lactation, pituitary function, and reproductive health.
Sex Steroid Hormones
DHEA-S (Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulphate): An androgen precursor produced by the adrenal glands, which plays a role in the production of sex hormones and impacts various bodily functions. Why measure: To evaluate adrenal gland function, assess androgen status, and diagnose conditions related to hormonal imbalances, such as adrenal insufficiency or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Oestradiol (Estradiol): A key form of estrogen important for regulating the menstrual cycle and reproductive health. Why Measure: To assess estrogen levels and diagnose hormonal disorders.
Testosterone: Main male sex hormone involved in male characteristics, muscle mass, and libido. Why Measure: To evaluate androgen levels and diagnose hormonal imbalances or conditions.
Free Testosterone (Calculated): The biologically active form of testosterone. Why Measure: To assess testosterone levels and diagnose hormonal imbalances.
Free Androgen Index (FAI): Ratio of total testosterone to SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin), indicating bioavailable testosterone. Why Measure: To evaluate androgen status and diagnose related hormonal disorders.
SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin): A protein that binds sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen. Why Measure: To assess hormonal balance and diagnose related disorders.
Stress Hormones
Cortisol: Primary stress hormone that regulates metabolism, immune response, and stress adaptation. Why Measure: To evaluate stress levels, adrenal function, and overall hormonal balance.
Thyroid Function
FT3 (Free Triiodothyronine): The unbound form of T3 hormone that is active in regulating metabolism and energy levels. Why measure: To assess thyroid function and diagnose thyroid disorders.
FT4 (Free Thyroxine): The unbound form of T4 hormone that helps regulate metabolism and growth. Why measure: To evaluate thyroid function and diagnose thyroid-related conditions.
TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): A hormone that regulates the production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) by the thyroid gland. Why measure: To evaluate thyroid function and diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Vitamins and Minerals
Active B12: The form of vitamin B12 that is available for use by the body, essential for blood cell production and nerve function. Why measure: To assess vitamin B12 levels and diagnose deficiencies or related conditions.
Magnesium: A mineral important for muscle and nerve function, bone health, and energy production. Why measure: To assess magnesium levels and diagnose deficiencies or related health conditions.
Vitamin D: Vital for calcium absorption and bone health, playing a key role in maintaining bone density. Why measure: To assess and support optimal bone health and calcium metabolism.
Serum Folate (Vitamin B9): A vitamin important for DNA synthesis and cell division, and crucial for preventing certain birth defects. Why measure: To evaluate folate levels and diagnose deficiencies or related health issues.
FAQ
All your questions. Answered.
Why do we offer more health markers at affordable prices?
We are dedicated to the importance of regular testing and understanding your body's changes over time. Limiting tests to a few markers or imposing high costs compromises this vital process.
Fingerprick testing presents significant challenges, which is why we exclusively offer samples collected by a phlebotomist at the most affordable prices. Our comprehensive testing includes a wide range of markers.
Join us in our mission to empower more people to gain meaningful health insights over time.
Why don't you offer fingerprick testing?
Fingerprick testing is both unreliable and often an unpleasant experience, as anyone who has tried to squeeze blood into small tubes will testify. Squeezing actually leads to invalid markers, as it affects the sample quality.
Additionally, due to the high volume of markers we offer, a fingerprick sample would further reduce the quality of the results. Therefore, we do not offer fingerprick testing.
Tell me more about the blood collection service
Once you have placed an order, we will contact you to find a suitable time and location for your blood sample collection. If you have any special requests, please let us know when we contact you.
The nurses/phlebotomists usually work in the NHS and work for Lola part-time for additional income. They are all very kind, experienced, and extremely well-vetted.
How should I prepare and what happens after the blood collection?
Before Your Blood Collection:
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to make the blood draw easier.
- Stay Warm: Use warm clothes or a heating pad to improve blood flow.
- Pets: Keep pets away during the blood draw to avoid any interruptions.
- Location: Choose a well-lit area, like a kitchen table or a comfy chair, for the procedure.
- Special Needs: Inform us of any past issues or special requirements you may have.
After the Procedure:
- Apply Pressure: Press the wound for at least 2 minutes to stop bleeding.
- Keep Dressing On: Leave the dressing on for at least 1 hour to prevent infection.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Don’t overuse your arm for the rest of the day to avoid strain.
Watch for These Signs:
- Excessive Bruising: Apply pressure and ice. The bruising should subside in a few days.
- Continued Pain: Use an ice pack for swelling. Persistent pain is rare but possible.
- Continued Bleeding: Apply strong pressure for at least 10 minutes. Call 999 if you feel lightheaded.
Now, your blood sample will be sent by our phlebotomist to the NHS-accredited lab. Once processed, it will be reviewed by our doctors and will be sent to you with a tailored review.
How accurate are the tests?
We only use UK government-approved NHS labs for the blood analysis, ensuring the same high level of accuracy at 99.8%, provided the sample is posted the same day using our Tracked 24 service. The phlebotomist will post the sample for you when they leave.
For this reason, we aim to schedule blood sample collection appointments with you from Monday to Wednesday.
Does a doctor review my results?
Our team of doctors reviews all blood results and provides a comprehensive written analysis, highlighting any markers that fall outside the normal range.
Results within 2 Working Days of Lab receiving the sample
Experience fast and reliable testing with results delivered within 2 working days. Upon receiving your order, we promptly dispatch your kit via Tracked 24 service. Our dedicated admin team will contact you the same day to schedule the phlebotomy appointment. The phlebotomist will collect your sample and then send the kit to the lab using Tracked 24 service. Once the lab receives the kit, your results will be ready within 2 working days.
How do I get the results?
Results are emailed as well as viewable in our Apple and Android apps. The apps can show trends over time as you take more tests.
Can I download my results to share with my GP?
Yes, you can download your results from the mobile app as a PDF or CSV to share with your GP.
What are the policies on cancellations and refunds?
For more information, please visit Refund & Cancellation
Do you show boundaries/ranges in your results?
Yes, all our biomarkers come with the ranges that are normal for your gender and age. Our doctor will also review your results and comment if anything is out of range.
How fast will my at-home phlebotomy service be?
As soon as we receive an order you will receive an email from us asking for dates/times that work for you. You will be offered an appointment within a few days of ordering allowing for the kit to arrive at your house which the phlebotomist will use.
Does the phlebotomist send my kit to the lab?
Yes, the nurse/phlebotomist will send your kit to the lab for analysis.
Are there any additional costs?
No, the phlebotomy appointment and doctor review are all included as part of the price.
What do I have to do before and after my Phlebotomy Visit?
Before Your Blood Collection:
- Hydrate: Drink 6-8 cups of water 2 hours before your appointment. This will make the blood draw easier.
- Fasting should be done if the test contains a Full Blood Count:
- Early Morning Collection - Skip breakfast until after the blood sample collection
- Late Morning Onwards Collection - Have a light meal and fast for at least 3-4 hours before taking the blood sample
- Stay Warm: Use warm clothes or a heating pad to improve blood flow.
- Pets: Keep pets away during the blood draw to avoid any interruptions.
- Location: Choose a well-lit area like a kitchen table or a comfy chair for the procedure.
- Special Needs: Inform us of any past issues or special requirements you may have.
After the Procedure:
- Apply Pressure: Press the wound for at least 2 minutes to stop bleeding.
- Keep Dressing On: Leave the dressing on for at least 1 hour to prevent infection.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Don’t overuse your arm for the rest of the day to avoid strain.
Watch for These Signs:
- Excessive Bruising: Apply pressure and ice. The bruising should subside in a few days.
- Continued Pain: Use an ice pack for swelling. Persistent pain is rare but possible.
- Continued Bleeding: Apply strong pressure for at least 10 minutes. Call 999 if you feel lightheaded.
Buying for someone else?
We understand that you may occasionally wish to purchase a test for another person. While direct purchases on behalf of others aren’t available, the easiest alternative is to buy one of our gift cards, valid for 12 months. You can get a gift card here.
If you’ve accidentally ordered a test under your account for someone else or need to transfer an order, please contact us at 0333 242 1288 as soon as possible before the sample is collected—so we can reassign the test to the correct individual.